Cotton fabric is a natural fabric made from the fibers of the cotton plant. Cotton fabric is the most widely used natural fabric, and has been used for thousands of years, originating during the Bronze age in what is now Pakistan.
This soft, affordable fabric is durable and absorbent, making it a versatile fabric that’s favored in clothing production.
This article will teach you everything you need to know about cotton, including its uses, advantages, history, and production.
What Is Cotton Fabric?
Cotton is a natural fiber, meaning it comes from plants. Other examples of natural fiber fabrics include wool, linen, and silk. Natural fibers differ from synthetic fibers, made from artificial materials like polyester or nylon.
Cotton fabric is made from the fibers of the cotton plant. The cotton plant is a shrub that’s native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
You typically propagate cotton plants through seeds. Once the plant grows tall enough, the cotton bolls will begin to form. Cotton bolls are the seed pods of the cotton plant, and inside these bolls are the Cotton fibers.
The cotton plant supplies longer fibers than any other natural fiber. The fibers’ length is one reason cotton is so popular for fabric manufacturing. Companies can easily spin cotton fibers into yarn or thread, which you can use to craft knitted or woven cotton fabric.
Cotton fabric is a very soft, absorbent, and breathable fabric. Some common applications of cotton are shirts, underwear, and towels.
Cotton Types
Two varieties of cotton are widely available: upland/Mexican cotton, and Egyptian cotton. Upland Cotton has a high yield, making it easy to produce and distribute. This cotton comes from Central and South America. Egyptian cotton is known for its luxurious feel and high price point.
Two other cotton varieties include Indian cotton, and Levant cotton.
History of Cotton Fabric
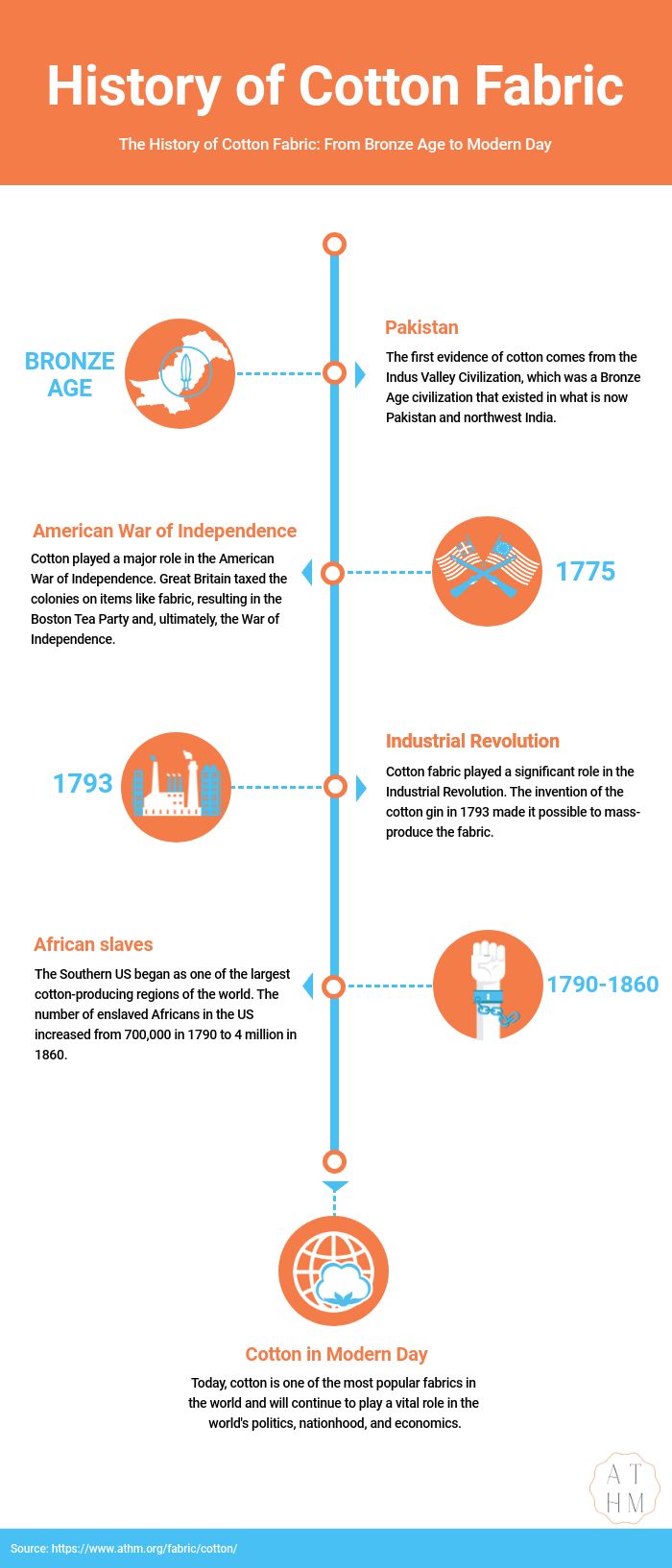
Cotton has a long history, as humans have used cotton fabric for centuries. The origin of cotton can be traced back to the Bronze Age, in what is now Pakistan. Cotton was popular in Europe through the Middle Ages, and played a big role in the Industrial Revoluion and the American slave trade.
Cotton’s Origins
The first evidence of cotton comes from the Indus Valley Civilization, which was a Bronze Age civilization that existed in what is now Pakistan and northwest India.
Ancient Egypt and Rome widely used this fabric. Europe was not exposed to cotton until the Middle Ages. At first, cotton was only used for currency because it was so valuable. Eventually, the cotton fabric became more widely available and was used to make clothing and other items.
The fortunes and nationhood of parts of the world depended on cotton’s importance. The southern parts of the United States were agricultural, and cotton was a cash crop. And in India, cotton fabric was and still is a significant part of the culture.
Cotton played a major role in the American War of Independence. Great Britain taxed the colonies on items like fabric, resulting in the Boston Tea Party and, ultimately, the War of Independence.
Cotton and the Industrial Revolution
Cotton fabric played a significant role in the Industrial Revolution. The invention of the cotton gin in 1793 made it possible to mass-produce the fabric.
The cotton gin is a machine that removes the cotton fibers and seeds from the cotton bolls, making it possible to produce cotton more quickly and efficiently. Before the invention of the cotton gin, removing cotton seeds was a labor-intensive process.
The Industrial Revolution led to an increase in the use of cotton. Nations built more factories to produce cotton fabric, and more people began to wear clothing made from cotton.
The importance of cotton during the Industrial Revolution would cause a second collision between US history and cotton. Following the Revolutionary War, the Southern US began as one of the largest cotton-producing regions of the world. Unfortunately, the Southern United States built its economy upon the backs of enslaved people.
The cotton gin had made it possible to mass-produce cotton fabric, but it also contributed to the mass production of slavery.
As a result, the number of enslaved Africans in the US increased from 700,000 in 1790 to 4 million in 1860. Cotton production also increased during this time. The US became the world’s largest cotton producer by 1820.
The morality of slavery was constantly a source of contention in the United States. Eventually, Americans fought a civil war over Southern states’ right to continue holding enslaved people and perpetuating an agricultural economy based on cotton production through slave labor.
Cotton Around the World
Cotton would play not only a role in the history of the US but also in the history of other countries. For example, cotton has been grown and used in India for centuries.
Cotton was so crucial to the Indian economy that Indians used it as currency at one point. Cotton is still an essential part of Indian culture and is used to make a variety of traditional garments.
Cotton is also a crucial part of the Chinese economy. China is the world’s largest cotton producer and consumer, and the cotton industry employs millions of people in China and contributes to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP).
Today, cotton is one of the most popular fabrics in the world and will continue to play a vital role in the world’s politics, nationhood, and economics.
Properties and Characteristics of Cotton Fabric
Cotton fabric has many desirable properties, for example: Cotton is a soft and breathable fabric It is absorbent, wrinkle resistant, and holds dye well. See cottons properties and characteristics below:
- Strong and durable: Cotton is less likely to tear or fray than other fabrics.
- Machine Washable: Cotton’s durability also makes it good for machine washing.
- Absorbency: Cotton is naturally very absorbent, making it a good option for towels, shorts, cotton swabs, cotton balls, and oil filters.
- Holds dye well: Cotton’s absorbency makes it good for dye and ink.
- Doesn’t conduct static: Cotton tends to absorb moisture from the air, making it a sligh conductor of electricity, leading to fewer excess electrons and less static electricity.
Types of Cotton Fabric
Different types of cotton fabric include denim, chambray, corduroy, flannel, knit, poplin, seersucker, and twill. Every kind of cotton fabric has its unique properties and uses.
Denim
Denim, a cotton by-product, is a sturdy fabric used to make jeans and often features diagonal ribbing.
Chambray
Chambray is a thin fabric that’s similar to denim but lighter in weight.
Corduroy
Corduroy is a cotton fabric with raised vertical lines or cords; companies use it to make garments and upholstery.
Flannel
Flannel is a fabric that has a soft, fuzzy surface. Many people use it to produce pajamas and blankets.
Knit Cotton
Knit Cotton is manufactured by interlocking loops of cotton thread. It’s stretchy and comfortable to wear.
Poplin
Poplin is a cotton fabric with a smooth surface and a slightly raised weave, and companies often use it to make shirts, skirts, and dresses. The fabric is also known as tabinet and has a characteristically silky feel.
Seersucker
Seersucker is a cotton blend fabric that has a wrinkled surface. The wrinkled surface makes it perfect for warm-weather garments since it’s also lightweight.
Twill
Twill is a cotton fabric that has a diagonal weave. You can use this type of cotton fabric to manufacture shirts, pants, and jackets.
How Is Cotton Fabric Made?
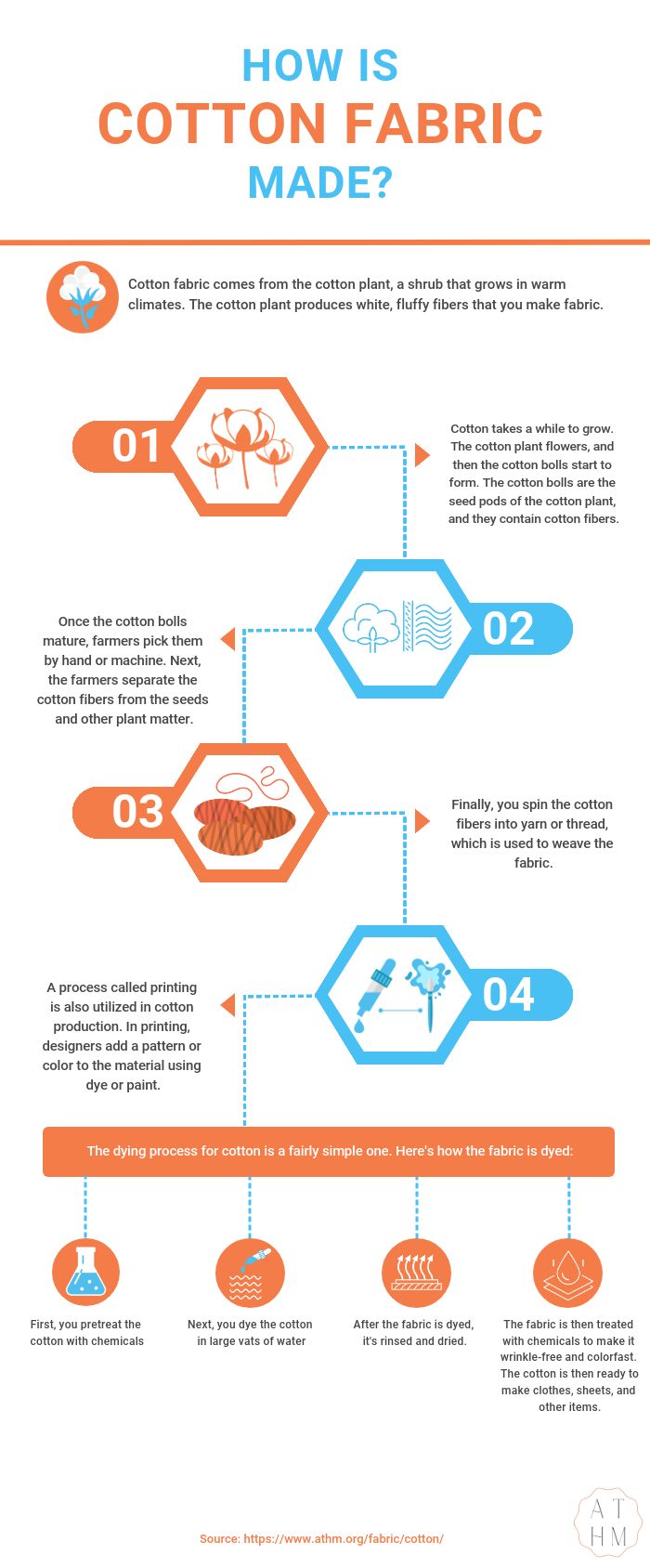
Cotton fabric comes from the cotton plant, a shrub that grows in warm climates. The cotton plant produces white, fluffy fibers that you make fabric.
Cotton takes a while to grow. The cotton plant flowers, and then the cotton bolls start to form. The cotton bolls are the seed pods of the cotton plant, and they contain cotton fibers.
Once the cotton bolls mature, farmers pick them by hand or machine. Next, the farmers separate the cotton fibers from the seeds and other plant matter.
Finally, you spin the cotton fibers into yarn or thread, which is used to weave the fabric.
A process called printing is also utilized in cotton production. In printing, designers add a pattern or color to the material using dye or paint.
The dying process for cotton is a fairly simple one. Here’s how the fabric is dyed:
- First, you pretreat the cotton with chemicals
- Next, you dye the cotton in large vats of water
- After the fabric is dyed, it’s rinsed and dried.
- The fabric is then treated with chemicals to make it wrinkle-free and colorfast. The cotton is then ready to make clothes, sheets, and other items.
Cotton is easy to care for. Cotton apparel can be machine washed and dried. Avoid exposure to sunlight or heat when storing cotton fabric, as this can cause the fabric to fade.
How Is Cotton Fabric Used?
You can use cotton to make various items, including outerwear, accessories, and blankets. Cotton is also often used to make cleaning supplies because it can absorb spills and dirt.
Cotton fabric is a popular choice for blankets and sweaters as it’s soft and breathable. It also makes cleaning cloths, cotton swabs, and oil filters.
A byproduct of cotton production, cottonseed oil, is also used in the cosmetics industry and to produce salad dressings and spreads.
Advantages of Cotton Fabric
The main advantage of cotton is that it is absorbent. Cotton fabric’s ability to absorb liquid makes it an ideal choice for shirts, shorts, and other items that come into contact with the skin. Since cotton is durable and less likely to fray, it’s used in affordable, everyday clothing.
Cotton fabric can be easily cleaned and dried. It is also resistant to wrinkles, making it a good choice for travel clothes. Cotton is a popular choice for many applications because it is absorbent, durable, and easy to care for.
Disadvantages of Cotton Fabric
The main disadvantage of cotton is that it shrinks when you wash it with hot water. Shrinking can cause cotton to become misshapen or too small for its intended purpose.
Cotton fabric is also susceptible to staining. Staining can be problematic if you use cotton fabric for items that come into contact with the skin. To avoid staining, it’s vital to pretreat any stains before washing the cotton.
Thinner types of cotton can also tear more easily than other fabrics.
Finally, cotton is highly flammable. It’s not usable in industrial processes that may expose it to fire. As such, you can’t use cotton to produce safety clothing or equipment.
Alternatives to Cotton Fabric
There are many alternatives to cotton, including polyester, nylon, and acrylic. These synthetic fabrics are less absorbent than cotton but are easier to care for. In general, polyester, nylon, and acrylic are less likely to shrink when washed in hot water.
Cotton Fabric vs. Polyester
Polyester is one of the most popular artificial fibers in the world. The rise of polyester in the 20th century negatively impacted the cotton industry.
Polyester is a synthetic fabric, while cotton is a naturally occurring one. Polyester is also different from cotton as it’s:
- Less likely to stain
- Less absorbent
- Not prone to shrinkage
- Heavier
- Less breathable
- Stretchier
Overall, polyester is a better choice for garments that need to be extra durable.
Cotton Fabric vs. Nylon
The most significant difference between cotton and nylon is that cotton is a natural fiber, and nylon is synthetic. Nylon is less absorbent, more durable, and less likely to shrink than cotton.
Nylon is generally used for industrial uses, while you traditionally use cotton for consumer goods and clothes.
Cotton Fabric vs. Acrylic
Cotton and acrylic are two standard fabrics used in yarn production. They are both popular but significantly different. Cotton is a natural fabric, while acrylic is an artificial one.
Acrylic is more popular than cotton because it’s affordable and easier to dye. As a result, you can find acrylic in almost any color. It is also hypoallergenic, and it holds its shape.
On the other hand, cotton is more expensive than acrylic. However, many people find cotton more appealing because of its softness. Additionally, it’s a more rugged fabric and will hold up to regular use far better than acrylic.
Natural Alternatives to Cotton Fabric
In addition to synthetic alternatives, there are also natural alternatives to cotton. Natural options include linen and hemp. Both of these fabrics are durable and absorbent. They are also less likely to shrink when washed in hot water.
Linen is made from the flax plant, while hemp comes from the Cannabis sativa plant. Both of these plants are grown for their fibers. Linen is more expensive than hemp because it is more challenging to produce.
Hemp is a strong fabric that you can use in sails and ropes. You can also use it to make paper and clothing. Hemp is affordable and widely available. It’s also mold-resistant, anti-microbial, and resilient to fiber degradation caused by washing.
Where Is Cotton Fabric Produced?
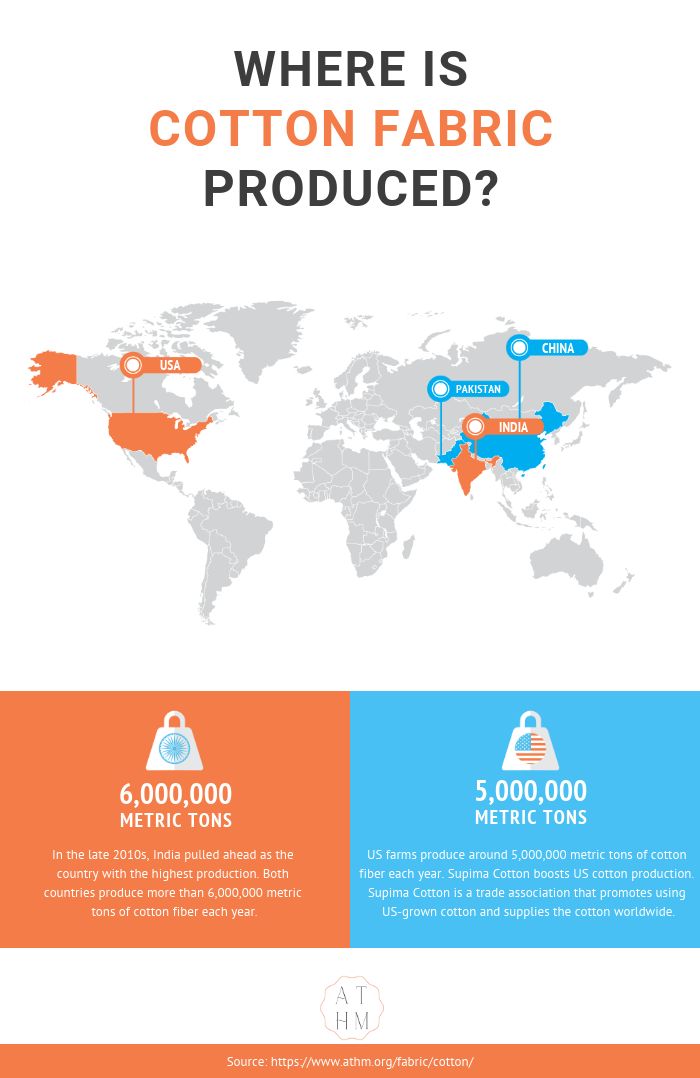
The fabric is produced worldwide, including in:
- The United States
- India
- China
- Pakistan
India and China often swap positions as the top two cotton-producing nations in the world. However, in the late 2010s, India pulled ahead as the country with the highest production. Both countries produce more than 6,000,000 metric tons of cotton fiber each year.
The US is a distant third in this competition, and US farms produce around 5,000,000 metric tons of cotton fiber each year. Supima Cotton boosts US cotton production. Supima Cotton is a trade association that promotes using US-grown cotton and supplies the cotton worldwide.
How Much Does Cotton Fabric Cost?
The cost of the fabric varies depending on the quality of the material and the amount of cotton used. You can purchase cotton fabric for as little as $2 per yard or as much as $30 per yard.
What Certifications Are Available for Cotton Fabric?
There are many different types of certifications available for cotton. Some focus on growing the textile, while others emphasize production and manufacturing.
Organic Cotton
The Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) is the most common certification for cotton fabric. GOTS-certified cotton fabric is at least 95% organic cotton. The material must also meet other criteria, such as being produced in a facility that uses environmentally and socially responsible practices.
Cotton fabric that is not GOTS certified can still be organic cotton. However, it will not have the same level of assurance as GOTS-certified cotton fabric.
Fairtrade Cotton
Another common certification for cotton is fair trade cotton. Fairtrade cotton is grown and produced according to fair trade standards. Fairtrade cotton is typically more expensive than other types of cotton.
Organic Content Standard (OCS)
Cotton fabric can also be certified by the Organic Content Standard (OCS). The OCS certifies that a product contains a certain percentage of organic cotton, but the certification doesn’t have any requirements for other aspects of the production process.
Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production (WRAP)
Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production (WRAP) is another socially conscious cotton certification pertaining to manufacturing cotton products. This certification looks at eradicating forced labor and child labor, as well as improving working hours, conditions, and wages.
What Is the Environmental Impact of Cotton Fabric?
Cotton fabric production has a significant environmental impact and a tremendous effect on freshwater resources, the soil, and pollution worldwide.
Cotton Fabrics Impact on Freshwater
Cotton is a water-intensive crop, and the irrigation of cotton fields can lead to water scarcity. An estimated 600 gallons of fresh water is needed to produce a single cotton t-shirt. That is the same amount of water a human drinks in 2.5 years.
In addition to the water needed to grow and produce cotton, the dying of cotton fabrics is also a water-intensive process. Over 1.2 trillion gallons of water are used yearly to dye cotton fabrics.
Using fresh water to grow and produce cotton is a tremendous problem. Surface water resources are steadily shrinking due to high levels of agriculture. For example, India uses an estimated 97% of the Indus river for irrigating cotton fields.
Cotton’s Impact on The Land
Cotton is also a soil-depleting crop. Cotton is a monocultural crop, and farmers do not rotate monocultural crops. Over time, successive cotton crops deplete the soil of its resources. The depletion of minerals and nutrients forces the farmers to cultivate new land.
The expansion of cotton fields directly leads to deforestation and habitat loss for wild animals. Additionally, this expansion can cause erosion problems. As trees are cut and cleared for new farmland, the chances of flash flood dramatically increase. Flash floods pose a danger to humans as well as wildlife.
Flash floods can dramatically impact rivers and streams by increasing the amount of particulate matter and pesticides in the water.
Pollution From Cotton Apparel Fabric
Pesticides are also commonly used on cotton crops. Cotton farming uses high amounts of insecticides and pesticides. These chemicals can pollute surface and groundwater resources. They can also harm the environment and human health.
The pesticides and insecticides used in cotton production are known human carcinogens and toxic to bees. The decrease in the bee population negatively impacts agriculture worldwide and destabilizes the global food system.
Cotton production is also a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions. In fact, cotton production is responsible for 2.4% of all global greenhouse gas emissions.
Cotton also requires large amounts of synthetic fertilizer. The use of synthetic fertilizer releases nitrous oxide into the environment. Nitrous oxide is one of the most potent greenhouse gasses and is over 300 times worse than carbon dioxide.
The transportation of cotton fabrics also has an environmental impact. Companies often ship cotton fabric long distances from where they produce it. The long distance between production and sales contributes to air pollution and climate change.
Conclusion
Cotton fabric is a popular choice for a large selection of applications because it’s absorbent, strong, soft, and easy to care for. However, the affordable cotton fabric does have some disadvantages, such as shrinking and staining.
When choosing cotton fabric for your next project, remember its porous nature, strength, and easy care. The textile has a long, complex history, and its production has various impacts on the world today, including contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.